Standard Practise Questions
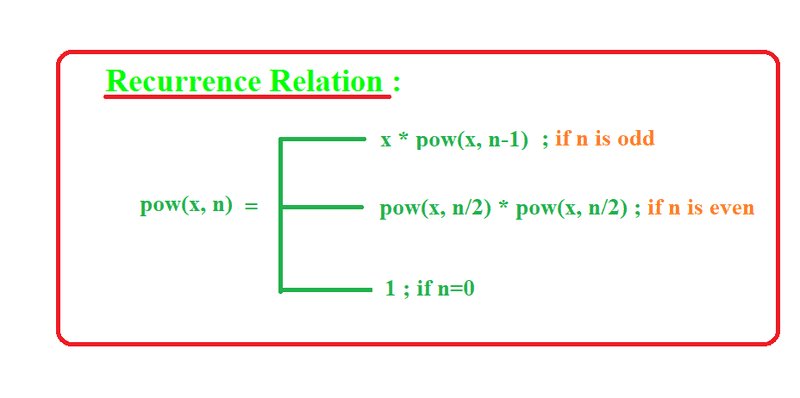
Q1 : Recursive Solution of Pow(x, n)
Implement pow(x, n)
which calculates x raised to the power n i.e. x^n
Example 1:
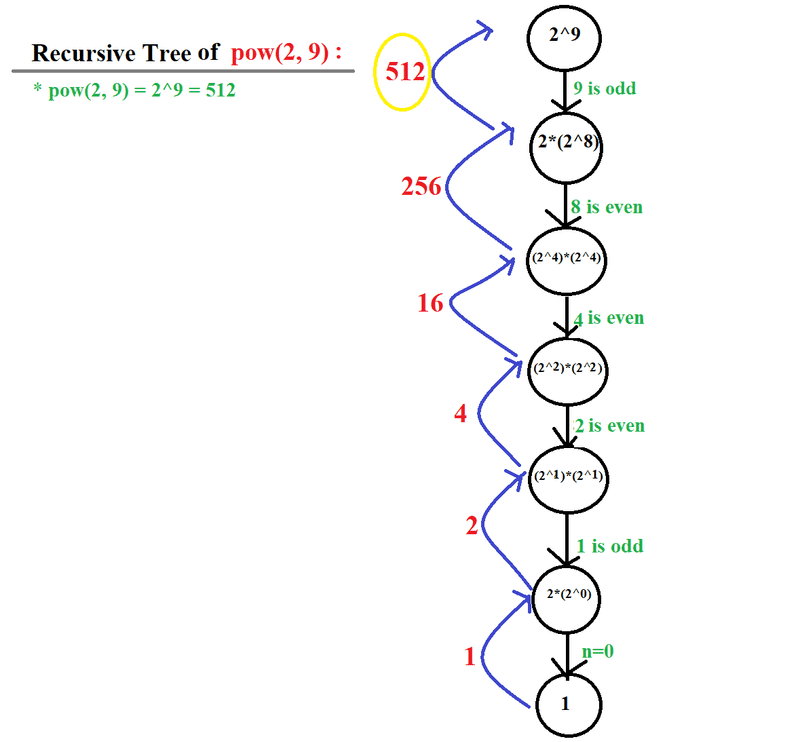
Input: x = 2, n = 9
Output: 512Example 2:
Input: x = 5, n = 3
Output: 125Solution & Approach :
Rcursive Tree : For, pow(2, 9) = 29
Time Complexity :
O(log(n))
Code :
class PowerProgram {
// power function
public static int pow(int x, int n){
if (n==0) return 1;
else if(n%2==0) {
int temp = pow(x, n/2);
return temp*temp;
}
else return x*pow(x, n-1);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 2, x = 9;
int result = pow(n, x);
System.out.print(result);
}
}
Output :
512Q2 : Recursive program to find all Indices of a Number from an Array
Given an array arr of size N and an integer X. The task is to find all the indices of the integer X in the array
Examples:
Input: arr = {1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 5}, X = 2
Output: 1 3 4
As Element 2 is present at indices 1, 3, 4 (0 based indexing)Solution & Approach :
-
If the start index reaches the length of the array, then return empty array
-
Else keep the first element of the array with yourself and pass the rest of the array to recursion.
-
If the element at start index is not equal to x then just simply return the answer which came from recursion.
-
Else if the element at start index is equal to x then shift the elements of the array (which is the answer of recursion) one step to the right and then put the start index in the front of the array (which came through recursion)
Code :
public class FindAllIndices {
public static int[] printAllIndex(int[] input, int x, int startIndex) {
if (startIndex == input.length) {
int[] output = new int[0];
return output;
}
int[] smallOutput = printAllIndex(input, x, startIndex + 1);
if (input[startIndex] == x) {
int[] output = new int[smallOutput.length + 1];
output[0] = startIndex;
for (int i = 0; i < smallOutput.length; i++) {
output[i + 1] = smallOutput[i];
}
return output;
} else {
return smallOutput;
}
}
public static int[] printAllIndex(int[] input) {
return printAllIndex(input, 2, 0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 5 };
arr = printAllIndex(arr);
for (int j : arr) {
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
}
}Output :
1 3 4Q3 : Count Good Numbers
A digit string is good if the digits (0-indexed) at even indices are even and the digits at odd indices are prime (2, 3, 5, or 7).
- For example,
2582is good because the digits(2 and 8)at even positions are even and the digits(5 and 2)at odd positions are prime. However,3245is not good because3is at an even index but is not even.
Given an integer n, return the total number of good digit strings of length n. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 10^9+7.
A digit string is a string consisting of digits 0 through 9 that may contain leading zeros.
Example-1
Input: n = 1
Output: 5
Explanation: The good numbers of length 1 are "0", "2", "4", "6", "8".Example-2
Input: n = 50
Output: 564908303Solution & Approach :
Code :
class GoodNumber {
static int mod=(int)1e9+7;
public static int countGoodNumbers(long n) {
if(n%2==0){
long a= power(4,n/2);
long b=power(5,n/2);
long z=a*b %mod;
return (int)(z);
}else{
long a= power(4,n/2);
long b=power(5,(n/2)+1);
long z=a*b%mod;
return (int)(z);
}
}
// power function
public static long power(long x,long y){
long temp;
if(y==0) return 1;
temp=power(x,y/2);
if(y%2==0) return (temp*temp)%mod;
else return (x*temp*temp)%mod;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 1;
int result = countGoodNumbers(n);
System.out.print(result);
}
}Output :
5
Happy Learning 👍