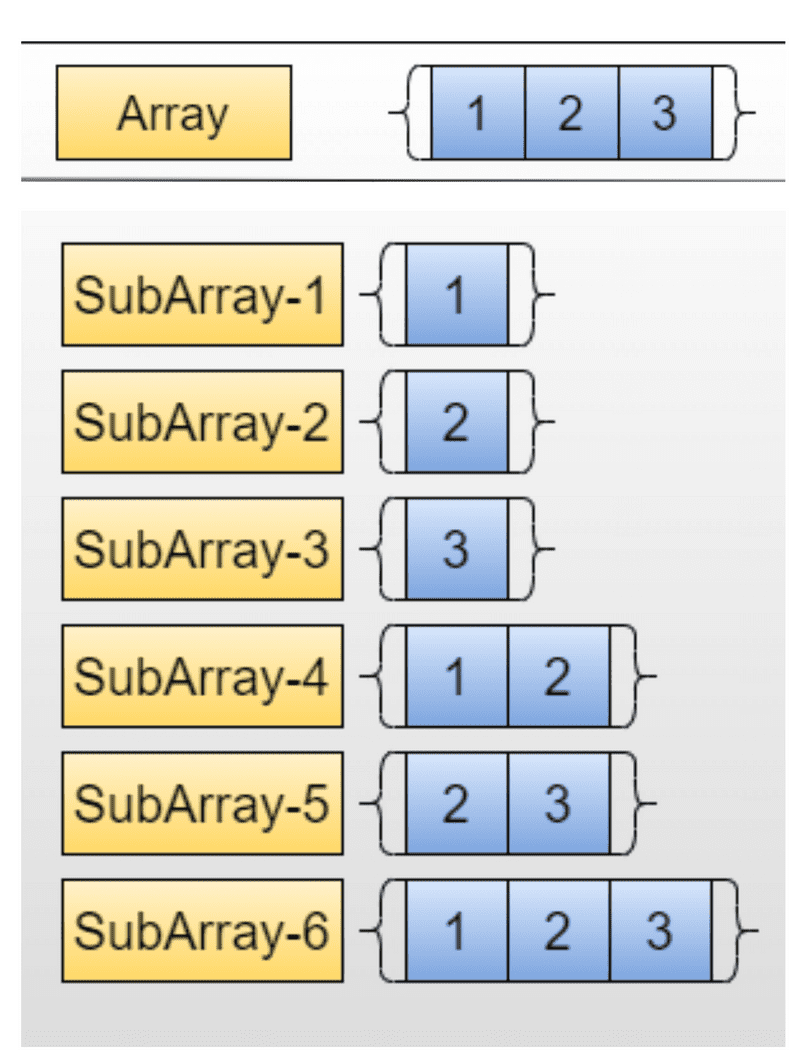
Subarrays
A subarray is a contiguous part of any given array. Basically speaking, an array that is present inside another array or a part of that array, but in a continuous manner.
For eg., consider the array [1, 2, 3, 4], There are 10 non-empty sub-arrays in this. The subarrays are [1], [2], [3], [4], [1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [1,2,3], [2,3,4] and [1,2,3,4]. In general, for an array/string of size n, there are n*(n+1)/2 non-empty subarrays/substrings.
How to generate all subarrays?
- We can run two nested loops
- The outer loop picks the starting element.
- The inner loop considers all elements on right of the picked starting element as ending element of subarray.
class Test
{
static int arr[] = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4};
// Prints all subarrays in arr[0..n-1]
static void subArray( int n)
{
// Pick starting point
for (int i=0; i <n; i++)
{
// Pick ending point
for (int j=i; j<n; j++)
{
// Print subarray between current starting
// and ending points
for (int k=i; k<=j; k++)
System.out.print(arr[k]+" ");
}
}
}
// Driver method to test the above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("All Non-empty Subarrays");
subArray(arr.length);
}
}Output -
All Non-empty Subarrays 1 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 2 2 3 2 3 4 3 3 4 4 Time Complexity: O(n^2)
Generating subarrays using recursion
Input : [1, 2, 3] Output : [1], [1, 2], [1, 3], [2], [1, 2, 3], [2, 3], [3]
Input : [1, 2] Output : [1], [1, 2], [2]
Approach
- We use two pointers, NAMELY,
startandendto maintain the starting and ending point of the array and follow the steps given below: - Stop if we have reached the end of the array
- Increment the
endindex ifstarthas become greater than theendindex. - Print the subarray from the
startindex to theendindex and increment thestartindex.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
class solution
{
// Recursive function to print all possible subarrays
// for given array
static void printSubArrays(int []arr, int start, int end)
{
// Stop if we have reached the end of the array
if (end == arr.length)
return;
// Increment the end point and start from 0
else if (start > end)
printSubArrays(arr, 0, end + 1);
// Print the subarray and increment the starting point
else
{
System.out.print("[");
for (int i = start; i < end; i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+", ");
}
System.out.println(arr[end]+"]");
printSubArrays(arr, start + 1, end);
}
return;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int []arr = {1, 2, 3};
printSubArrays(arr, 0, 0);
}
}Output -
[1] [1, 2] [2] [1, 2, 3] [2, 3] [3]
**Time Complexity: O(n^2) **